The Experienced English Housekeeper: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (92 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:Cover Page TEEH.jpg|270px|thumb|Cover page of "The Experienced English Housekeeper," containing an image of author Elizabeth Raffald]] | |||
This entry analyzes six different copies of "The Experienced English Housekeeper" by Elizabeth Raffald located at the [https://www.library.upenn.edu/kislak Kislak Center for Special Collections] at the University of Pennsylvania. This cookbook contains over 900 recipes, such as peppermint water, pickled mushrooms, walnut ketchup, mulled wine, potted pigeons, fried celery, savory veal pie, and crawfish soup. | |||
The first copy was published in 1773 and is the Third Edition <ref name="TEEH4"> Raffald, Elizabeth, and R Baldwin. "The Experienced English Housekeeper." London: Printed for the author, and sold by R. Baldwin, No. 47, in Pater-Noster-Row, 1773. https://franklin.library.upenn.edu/catalog/FRANKLIN_9962183703503681 </ref>. The second copy was published in 1786 and is the Tenth Edition <ref name="TEEH6"> Raffald, Elizabeth. "The Experienced English Housekeeper." London: Printed for R. Baldwin, 1786. https://franklin.library.upenn.edu/catalog/FRANKLIN_9921958233503681 </ref>. The third copy was published in 1794 and is the Eleventh Edition <ref name="TEEH5"> Raffald, Elizabeth, and Robert Baldwin. "The Experienced English Housekeeper." London: Printed for R. Baldwin, 1794. https://franklin.library.upenn.edu/catalog/FRANKLIN_9976201983503681 </ref>. The fourth copy was published in 1799 and is the Twelfth Edition <ref name="TEEH1"> Raffald, Elizabeth, and R Baldwin. "The Experienced English Housekeeper." London: Printed for R. Baldwin, 1799. https://franklin.library.upenn.edu/catalog/FRANKLIN_9962129733503681 </ref>. The fifth copy was published in 1794 and is considered the New Edition <ref name="TEEH3"> Raffald, Elizabeth, William Osborne, and T Griffin. "The Experienced English Housekeeper." London: Printed for W. Osborne and T. Griffin, 1794. https://franklin.library.upenn.edu/catalog/FRANKLIN_9947852523503681 </ref>. The sixth copy was published in 1798 and is also considered the New Edition <ref name="TEEH2"> Raffald, Elizabeth, William Osborne, and T Griffin. "The Experienced English Housekeeper." London: Printed for W. Osborne and T. Griffin, 1798. https://franklin.library.upenn.edu/catalog/FRANKLIN_9947825983503681 </ref>. | |||
==Background== | ==Background== | ||
===Historical Context & Author=== | ===Historical Context & Author=== | ||
As a viral book of its time, | As a viral book of its time, "The Experienced English Housekeeper" by Elizabeth Raffald iterated over the years into new editions, each time offering readers access to more recipes and content. Raffald’s book was officially published in thirteen different editions, spanning from 1769 to 1806. Despite Raffald’s untimely death in 1781, her publishing team continued to produce new versions. In addition to the publications of the thirteen editions, Raffald’s book faced an active black market, resulting in the creation and sales of numerous [https://earlymodernfemalebookownership.wordpress.com/2020/11/02/elizabeth-raffald-the-experienced-english-housekeeper-1776-and-1789/ pirated editions] worldwide. The Kislak Center houses six copies total, with publication years of 1773, 1786, two from 1794, 1798, and 1799. These copies represent the Third Edition, Tenth Edition, Eleventh Edition, and Twelfth Edition, and two copies of “A New Edition,” which fall into the category of unauthorized publications. | ||
Author Elizabeth Raffald worked as a housekeeper in England in the eighteenth century in Doncaster, Cheshire, and Manchester, each approximately 200 miles | Author Elizabeth Raffald [https://englishhistoryauthors.blogspot.com/2019/04/elizabeth-raffald-martha-stewart-of.html worked as a housekeeper] in England in the eighteenth century in Doncaster, Cheshire, and Manchester, each approximately 200 miles from London. Raffald learned the recipes and tips in "The Experienced English Housekeeper" while employed as a talented housekeeper and chef in these locales. In addition to her housekeeping pursuits, as a skilled entrepreneur, Raffald owned and operated a confectionary business and specialized in baking <ref name="Culinary Biographies"> Arndt, Alice. "Culinary Biographies." First edition. Houston, Tex.: YES Press, 2006. https://franklin.library.upenn.edu/catalog/FRANKLIN_9940962533503681 </ref>. | ||
===Provenance=== | ===Provenance=== | ||
Each copy of | [[File:BookPlates TEEH.jpg|270px|thumb|Image of the inside cover of a copy of "The Experienced English Housekeeper" which contains bookplates from James Beard and Fritz Blank]] | ||
Each copy of "The Experienced English Housekeeper" stored at the Kislak Center at Penn tells its own provenance story. All six copies contain a variety of ownership marks that help to trace provenance. The [https://www.library.upenn.edu/detail/collection/chef-fritz-blank-culinary-archive-and-library Chef Fritz Blank Culinary Archive and Library] houses four of the six copies. [https://digitalbookhistory.com/culturesofthebook/Home_Economics_Foods_and_Food_Preparation#Chef_Fritz_Blank Fritz Blank] was a famous chef and restaurant owner in Philadelphia, and he donated several thousand cookbooks to Penn between 2002 and 2007. For the first two copies, provenance solely traces to Fritz Blank. However, for the third copy, Fritz Blank obtained the book from James Beard, the namesake of the famous [https://www.jamesbeard.org/ James Beard Foundation] and pioneer of American cooking television shows. Furthermore, the fourth copy contains a signature from Frances Wood in 1826 and collector’s stamps from Alfred Berry before arriving in Fritz Blank’s collection. The connection between Frances Wood, Alfred Berry, and Fritz Blank is unclear. The fifth copy was donated to Penn in 2010 by collector Robert Frost, who donated a few hundred books to the Kislak Center, with an emphasis on British literature. Lastly, Esther Aresty donated the sixth copy. As a cookbook historian, Aresty created the [https://www.library.upenn.edu/detail/collection/esther-b-aresty-collection-rare-books-culinary-arts Esther B. Aresty Collection of Rare Books on the Culinary Arts] at Penn in 1996, a collection of nearly 600 cookbooks with publication dates across five centuries. | |||
In addition to the provenance data, some | In addition to the provenance data, some former owners of "The Experienced English Housekeeper" left their marks on the books by inserting a bookplate. In particular, Fritz Blank, Esther Aresty, and James Beard included signature bookplates containing their names alongside representative images. As an interesting side note, Esther Aresty repurposed Elizabeth Raffald’s signature bookplate with some modifications as her personal bookplate, paying homage to Raffald. Readers can trace further ownership to booksellers through a binder’s ticket for Fox Bookbinder and a label from Corner Book Shop. Another hint of provenance can be associated with a printed dinner menu from Chef E. Bertsch, contained as ephemera inside one copy. | ||
[[File:Menu.jpg|270px|thumb|Menu from Chef E. Bertsch contained inside of a copy of "The Experienced English Housekeeper"]] | |||
===Publishing and Editions=== | ===Publishing and Editions=== | ||
Elizabeth Raffald initially published her book locally in Manchester with the support of Joseph Harrop, a printer who also ran the local newspaper, | Elizabeth Raffald initially published her book locally in Manchester with the support of [https://peoplepill.com/people/elizabeth-raffald Joseph Harrop], a printer who also ran the local newspaper, the [https://www.britishnewspaperarchive.co.uk/titles/manchester-mercury Manchester Mercury]. Soon after, with the ensuing popularity of her book, Raffald transitioned to working with Robert Baldwin, a famous publisher in London. Four of the six copies at the Kislak Center attribute publication to Robert Baldwin of Paternoster Row in London. However, the two unauthorized copies attribute publication to “W. Osborne & T. Griffin,” also located in London, but not having an official relationship with Raffald. | ||
[[File:Signature.jpg|270px|thumb|Image of the first page of text from "The Experienced English Housekeeper" with the cursive signature of Elizabeth Raffald]] | |||
In place of traditional copyrighting or licensing, the bottom of the cover page in each edition says “N. B. No Book is genuine but what is signed by the Author” and “Printed for the Author.” Then, the first page of the book’s first chapter contains a cursive | In place of traditional copyrighting or licensing, the bottom of the cover page in each edition says “N. B. No Book is genuine but what is signed by the Author” and “Printed for the Author.” Then, the first page of the book’s first chapter contains a cursive signature of the author. This copyrighting information is observed in the four official editions at the Kislak Center, whereas the two unauthorized copies do not include any form of protective note or signature. Furthermore, the official editions describe more details regarding the publisher than the unauthorized copies, such as by listing the year of publication. Searching for these essential lines on the cover page can help a reader to determine the authenticity of the specific copy of "The Experienced English Housekeeper." | ||
==Material Analysis== | ==Material Analysis== | ||
This book object is a traditional codex featuring a quarto format with an additional nested sheet. "The Experienced English Housekeeper" contains signature marks on the bottom of each page. The book is a standard novel with a rectangular shape that remains consistent from front cover to back cover. The text is printed on the front and back of each page. The decision to print the text suggests that Raffald and her publishing team sought to reach a wide audience of readers, unlike many handwritten cookbooks of the time. Amongst all the copies, the front of the book feels well-protected and well-preserved, with little evidence of aging throughout the past three centuries. However, upon opening the books, the aging stands out, as indicated by the yellowing and hardening of the off-white pages. In some copies, the pages face extreme wear and tear, such as the cover page in The Third Edition, which is nearly disintegrating. | |||
The hard cover over the book likely was made from dyed leather sourced from animals such as cows, goats, and sheep, which offer impressive durability, a smooth texture, and a pleasing aesthetic. Utilizing a hardcover implies that Raffald intended for her book to be used frequently over a long period of time, rather than read just once. The book’s interior contains paper, a popular and affordable substrate of the era. Specifically, "The Experienced English Housekeeper" includes nearly 400 pages of text printed in a serif font in a physically bumpy texture above the page. | |||
The | Every copy of "The Experienced English Housekeeper" is bound, contemporary in the style of the late eighteenth century. Interestingly, each copy at Kislak Center varies in binding and spine designs, likely bound by owners based on personal preferences. Specifically, the spine of each of the six copies of "The Experienced English Housekeeper" by Elizabeth Raffald displays a different variation upon the title and author’s name. The spines read “RAFFALD’S COOKERY BOOK,” “Raffald’s English Housekeeper,” “The English Housekeeper,” “English Housekpr. Raffald,” “English Housekeeper - Raffald - 1798,” and “The English Housekeeper - Mrs. Raffald.” Furthermore, the design varies, with one book bound by a black spine with a gilded border and another with a green spine interspersed with thick ridges. | ||
[[File:SpineTEEH.jpg|270px|thumb|Image of the spine of one copy of “The Experienced English Housekeeper” | |||
]] | |||
One unique structural attribute of the book, especially for the publication era, is incorporating fold-out papers, known as plates. The reader can fold out a couple of pieces of paper attached to the book’s binding, which expand to an engraving approximately the size of four individual pages. One fold-out in "The Experienced English Housekeeper" displays a detailed model of a fully-set dinner table, while another analyzes the functionality of cooking devices. | |||
[[File:FoldOut TEEH.jpg|270px|thumb|Image of a folded out guide to setting a dinner table, contained in "The Experienced English Housekeeper"]] | |||
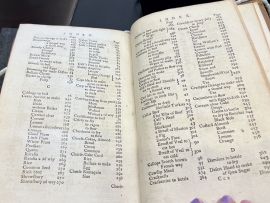
The | The cover page of each copy of "The Experienced English Housekeeper" contains a detailed overview describing the recipes in Part I, Part II, and Part III of the book, spanning the entire culinary range, from proteins to baked goods to wines. However, this table of contents of sorts lacks page numbers, so it serves more as a helpful description of the contents rather than a guide to finding each page. The book is split into chapters. Furthermore, each edition has an extremely detailed index consisting of fourteen pages. The index is very specific and functions like a grocery store catalog, listing every imaginable ingredient. The navigational tools throughout the book imply that readers benefit from general and specific guidance in the process of locating a precise recipe within a book that contains over 900. The overview and index support a faster reading process, while the lack of a true table of contents invites many readers to browse the book at their leisure. | ||
[[File:Index TEEH.jpeg|270px|thumb|Image of the index contained at the rear of "The Experienced English Housekeeper"]] | |||
The | |||
==Book Use== | ==Book Use== | ||
===Marginalia | ===Marginalia=== | ||
According to the local notes data provided by Penn Libraries, several copies of | [[File:Marginalia_TEEH.jpg|270px|thumb|Image of marginalia and marks in a copy of "The Experienced English Housekeeper" on a page containing a variety of vegetable recipes]] | ||
According to the local notes data provided by Penn Libraries, several copies of "The Experienced English Housekeeper" contain marginalia and annotations, presenting substantial evidence of readership. While the marginalia and annotations do not explicitly reference authorship, it can be inferred that most marks come from the book owners, who reviewed the included recipes as they cooked them. In one copy in particular, the owner deployed an internal rating system, writing next to the recipes feedback like “Good!” and “Very good,” an antiquated version of the rating systems used today by chefs on social media and mobile cooking applications. Other times, an owner may suggest adding missing ingredients to a recipe, such as ginger. Lastly, owners drew random doodles in the margins of some copies. Such marginalia and annotations suggest an interactive reading process in which the reader contributes opinions and perspectives alongside the author. The author’s opinion is tested, opposed, and approved. | |||
Unfortunately, beyond the marginalia and annotations, most of the ephemera contained in the copies of the book have been removed from Penn Libraries and stored separately, such as handwritten recipes, photocopies, correspondences, book dealer descriptions, and a child’s letter. | Unfortunately, beyond the marginalia and annotations, most of the ephemera contained in the copies of the book have been removed from Penn Libraries and stored separately, such as handwritten recipes, photocopies, correspondences, book dealer descriptions, and a child’s letter. | ||
===Marks=== | |||
Marks are prevalent throughout one copy of "The Experienced English Housekeeper" in which the book owner edited the included recipes to reflect personal preferences beyond the reviews referenced above. With many owners as famous chefs themselves, it makes sense for experimentation and revision of the traditional recipes from the eighteenth century, both in terms of technological advancement and changes in palettes. For example, in one copy, the owner crossed off some of the information contained in the recipes. Upon checking with other copies of the same book, it became apparent that the owner crossed out “cloves and nutmegs,” specific ingredients in a recipe. | |||
==Historical Significance== | ==Historical Significance== | ||
===Gender and Literature=== | ===Gender and Literature=== | ||
Raffald defines her target audience on the cover page of | Raffald defines her target audience on the cover page of "The Experienced English Housekeeper" declaring her book is “For the USE and EASE of Ladies, Housekeepers, Cooks, &C,” with "&C" meaning et cetera. She supports this claim with an explicit dedication to the Honorable Lady Elizabeth Warburton, Raffald’s most recent housekeeping client. After that, the book contains a substantial preface, likewise dedicated to Warburton. The dedication and preface are both clearly from the perspective of Raffald as they describe her personal experiences as a housekeeper for Warburton. Unlike other books of the time, Raffald writes as a woman, dedicated to a woman, and for a target audience of women. This female focus differentiates "The Experienced English Housekeeper," holding significance in the world of female authorship and publishing. | ||
Scholarly sources about "The Experienced English Housekeeper" indicate that the book serves as a tool to understand the lives of women in the domestic sphere in the eighteenth century. Readers learn about foods consumed, available technologies, and societal expectations. After all, many British women referred to "The Experienced English Housekeeper" as a cultural authority. In particular, the cookbook illuminates the emphasis on thriftiness and resourcefulness among women of the time, who frequently faced economic hardships and lack of financial control at home <ref name="Eat My Words"> Theophano, Janet. "Eat My Words: Reading Women’s Lives through the Cookbooks They Wrote." Palgrave, 2002.https://franklin.library.upenn.edu/catalog/FRANKLIN_9978848186403681 </ref>. Similarly, Raffald provides suggestions regarding cleanliness and order in the house, reinforcing traditional gender roles of the time <ref name="Knowledge and Taste"> Wall, Wendy. "Recipes for Thought: Knowledge and Taste in the Early Modern English Kitchen." University of Pennsylvania Press, 2016. https://franklin.library.upenn.edu/catalog/FRANKLIN_9978848186403681 </ref>. | |||
===Cultural Implications=== | ===Cultural Implications=== | ||
"The Experienced English Housekeeper" by Elizabeth Raffald boasts enormous cultural significance in England in the eighteenth century and beyond. The book circulated extremely widely as a bestseller of its era. Each copy of "The Experienced English Housekeeper" contains over 900 recipes, a massive collection, especially considering that cookbooks were not as common at the time. Many of these recipes were usually passed down within families, so a publication compiling them together served as a groundbreaking way to share cooking knowledge that previously never appeared in print. Furthermore, some famous British recipes, such as mince pies and Yorkshire puddings, first reached a widespread audience through Raffald's book <ref name="Culinary Biographies"> Arndt, Alice. "Culinary Biographies." First edition. Houston, Tex.: YES Press, 2006. https://franklin.library.upenn.edu/catalog/FRANKLIN_9940962533503681 </ref>. Therefore, Raffald spearheaded a number of culinary traditions, inspiring generations of chefs throughout England and the world. | |||
Additionally, "The Experienced English Housekeeper" had functions beyond cooking, providing advice on running a household, entertaining guests, and preparing for special occasions. Raffald's book marked a turning point in the genre of cookbooks, which previously solely focused on recipes <ref name="Invention of the Modern Cookbook"> Sherman, Sandra. "Invention of the Modern Cookbook." Santa Barbara, Calif.: Greenwood Press, 2010. https://franklin.library.upenn.edu/catalog/FRANKLIN_9978881984403681 </ref>. Accordingly, Raffald's book functions as a symbol of the evolution of cookbooks, demonstrating how enduring cultural identities form through distribution of such literature. | |||
Despite the female emphasis in "The Experienced English Housekeeper," the book likely circulated extensively in the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries, reaching an audience of readers that spanned gender, socioeconomic status, and geographic location. The book circulated through booksellers, libraries, and private sales. Unlike other books at the Kislak Center, "The Experienced English Housekeeper" was not rare; in fact, compared to most other books of its era, it was extremely accessible. The recent-looking marginalia from readers like Fritz Blank, Esther Aresty, and James Beard suggests that use cases for "The Experienced English Housekeeper" progressed well into the twentieth century and may even be applicable today. | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Latest revision as of 17:04, 2 May 2023

This entry analyzes six different copies of "The Experienced English Housekeeper" by Elizabeth Raffald located at the Kislak Center for Special Collections at the University of Pennsylvania. This cookbook contains over 900 recipes, such as peppermint water, pickled mushrooms, walnut ketchup, mulled wine, potted pigeons, fried celery, savory veal pie, and crawfish soup.
The first copy was published in 1773 and is the Third Edition [1]. The second copy was published in 1786 and is the Tenth Edition [2]. The third copy was published in 1794 and is the Eleventh Edition [3]. The fourth copy was published in 1799 and is the Twelfth Edition [4]. The fifth copy was published in 1794 and is considered the New Edition [5]. The sixth copy was published in 1798 and is also considered the New Edition [6].
Background
Historical Context & Author
As a viral book of its time, "The Experienced English Housekeeper" by Elizabeth Raffald iterated over the years into new editions, each time offering readers access to more recipes and content. Raffald’s book was officially published in thirteen different editions, spanning from 1769 to 1806. Despite Raffald’s untimely death in 1781, her publishing team continued to produce new versions. In addition to the publications of the thirteen editions, Raffald’s book faced an active black market, resulting in the creation and sales of numerous pirated editions worldwide. The Kislak Center houses six copies total, with publication years of 1773, 1786, two from 1794, 1798, and 1799. These copies represent the Third Edition, Tenth Edition, Eleventh Edition, and Twelfth Edition, and two copies of “A New Edition,” which fall into the category of unauthorized publications.
Author Elizabeth Raffald worked as a housekeeper in England in the eighteenth century in Doncaster, Cheshire, and Manchester, each approximately 200 miles from London. Raffald learned the recipes and tips in "The Experienced English Housekeeper" while employed as a talented housekeeper and chef in these locales. In addition to her housekeeping pursuits, as a skilled entrepreneur, Raffald owned and operated a confectionary business and specialized in baking [7].
Provenance

Each copy of "The Experienced English Housekeeper" stored at the Kislak Center at Penn tells its own provenance story. All six copies contain a variety of ownership marks that help to trace provenance. The Chef Fritz Blank Culinary Archive and Library houses four of the six copies. Fritz Blank was a famous chef and restaurant owner in Philadelphia, and he donated several thousand cookbooks to Penn between 2002 and 2007. For the first two copies, provenance solely traces to Fritz Blank. However, for the third copy, Fritz Blank obtained the book from James Beard, the namesake of the famous James Beard Foundation and pioneer of American cooking television shows. Furthermore, the fourth copy contains a signature from Frances Wood in 1826 and collector’s stamps from Alfred Berry before arriving in Fritz Blank’s collection. The connection between Frances Wood, Alfred Berry, and Fritz Blank is unclear. The fifth copy was donated to Penn in 2010 by collector Robert Frost, who donated a few hundred books to the Kislak Center, with an emphasis on British literature. Lastly, Esther Aresty donated the sixth copy. As a cookbook historian, Aresty created the Esther B. Aresty Collection of Rare Books on the Culinary Arts at Penn in 1996, a collection of nearly 600 cookbooks with publication dates across five centuries.
In addition to the provenance data, some former owners of "The Experienced English Housekeeper" left their marks on the books by inserting a bookplate. In particular, Fritz Blank, Esther Aresty, and James Beard included signature bookplates containing their names alongside representative images. As an interesting side note, Esther Aresty repurposed Elizabeth Raffald’s signature bookplate with some modifications as her personal bookplate, paying homage to Raffald. Readers can trace further ownership to booksellers through a binder’s ticket for Fox Bookbinder and a label from Corner Book Shop. Another hint of provenance can be associated with a printed dinner menu from Chef E. Bertsch, contained as ephemera inside one copy.

Publishing and Editions
Elizabeth Raffald initially published her book locally in Manchester with the support of Joseph Harrop, a printer who also ran the local newspaper, the Manchester Mercury. Soon after, with the ensuing popularity of her book, Raffald transitioned to working with Robert Baldwin, a famous publisher in London. Four of the six copies at the Kislak Center attribute publication to Robert Baldwin of Paternoster Row in London. However, the two unauthorized copies attribute publication to “W. Osborne & T. Griffin,” also located in London, but not having an official relationship with Raffald.

In place of traditional copyrighting or licensing, the bottom of the cover page in each edition says “N. B. No Book is genuine but what is signed by the Author” and “Printed for the Author.” Then, the first page of the book’s first chapter contains a cursive signature of the author. This copyrighting information is observed in the four official editions at the Kislak Center, whereas the two unauthorized copies do not include any form of protective note or signature. Furthermore, the official editions describe more details regarding the publisher than the unauthorized copies, such as by listing the year of publication. Searching for these essential lines on the cover page can help a reader to determine the authenticity of the specific copy of "The Experienced English Housekeeper."
Material Analysis
This book object is a traditional codex featuring a quarto format with an additional nested sheet. "The Experienced English Housekeeper" contains signature marks on the bottom of each page. The book is a standard novel with a rectangular shape that remains consistent from front cover to back cover. The text is printed on the front and back of each page. The decision to print the text suggests that Raffald and her publishing team sought to reach a wide audience of readers, unlike many handwritten cookbooks of the time. Amongst all the copies, the front of the book feels well-protected and well-preserved, with little evidence of aging throughout the past three centuries. However, upon opening the books, the aging stands out, as indicated by the yellowing and hardening of the off-white pages. In some copies, the pages face extreme wear and tear, such as the cover page in The Third Edition, which is nearly disintegrating.
The hard cover over the book likely was made from dyed leather sourced from animals such as cows, goats, and sheep, which offer impressive durability, a smooth texture, and a pleasing aesthetic. Utilizing a hardcover implies that Raffald intended for her book to be used frequently over a long period of time, rather than read just once. The book’s interior contains paper, a popular and affordable substrate of the era. Specifically, "The Experienced English Housekeeper" includes nearly 400 pages of text printed in a serif font in a physically bumpy texture above the page.
Every copy of "The Experienced English Housekeeper" is bound, contemporary in the style of the late eighteenth century. Interestingly, each copy at Kislak Center varies in binding and spine designs, likely bound by owners based on personal preferences. Specifically, the spine of each of the six copies of "The Experienced English Housekeeper" by Elizabeth Raffald displays a different variation upon the title and author’s name. The spines read “RAFFALD’S COOKERY BOOK,” “Raffald’s English Housekeeper,” “The English Housekeeper,” “English Housekpr. Raffald,” “English Housekeeper - Raffald - 1798,” and “The English Housekeeper - Mrs. Raffald.” Furthermore, the design varies, with one book bound by a black spine with a gilded border and another with a green spine interspersed with thick ridges.

One unique structural attribute of the book, especially for the publication era, is incorporating fold-out papers, known as plates. The reader can fold out a couple of pieces of paper attached to the book’s binding, which expand to an engraving approximately the size of four individual pages. One fold-out in "The Experienced English Housekeeper" displays a detailed model of a fully-set dinner table, while another analyzes the functionality of cooking devices.

The cover page of each copy of "The Experienced English Housekeeper" contains a detailed overview describing the recipes in Part I, Part II, and Part III of the book, spanning the entire culinary range, from proteins to baked goods to wines. However, this table of contents of sorts lacks page numbers, so it serves more as a helpful description of the contents rather than a guide to finding each page. The book is split into chapters. Furthermore, each edition has an extremely detailed index consisting of fourteen pages. The index is very specific and functions like a grocery store catalog, listing every imaginable ingredient. The navigational tools throughout the book imply that readers benefit from general and specific guidance in the process of locating a precise recipe within a book that contains over 900. The overview and index support a faster reading process, while the lack of a true table of contents invites many readers to browse the book at their leisure.
Book Use
Marginalia

According to the local notes data provided by Penn Libraries, several copies of "The Experienced English Housekeeper" contain marginalia and annotations, presenting substantial evidence of readership. While the marginalia and annotations do not explicitly reference authorship, it can be inferred that most marks come from the book owners, who reviewed the included recipes as they cooked them. In one copy in particular, the owner deployed an internal rating system, writing next to the recipes feedback like “Good!” and “Very good,” an antiquated version of the rating systems used today by chefs on social media and mobile cooking applications. Other times, an owner may suggest adding missing ingredients to a recipe, such as ginger. Lastly, owners drew random doodles in the margins of some copies. Such marginalia and annotations suggest an interactive reading process in which the reader contributes opinions and perspectives alongside the author. The author’s opinion is tested, opposed, and approved.
Unfortunately, beyond the marginalia and annotations, most of the ephemera contained in the copies of the book have been removed from Penn Libraries and stored separately, such as handwritten recipes, photocopies, correspondences, book dealer descriptions, and a child’s letter.
Marks
Marks are prevalent throughout one copy of "The Experienced English Housekeeper" in which the book owner edited the included recipes to reflect personal preferences beyond the reviews referenced above. With many owners as famous chefs themselves, it makes sense for experimentation and revision of the traditional recipes from the eighteenth century, both in terms of technological advancement and changes in palettes. For example, in one copy, the owner crossed off some of the information contained in the recipes. Upon checking with other copies of the same book, it became apparent that the owner crossed out “cloves and nutmegs,” specific ingredients in a recipe.
Historical Significance
Gender and Literature
Raffald defines her target audience on the cover page of "The Experienced English Housekeeper" declaring her book is “For the USE and EASE of Ladies, Housekeepers, Cooks, &C,” with "&C" meaning et cetera. She supports this claim with an explicit dedication to the Honorable Lady Elizabeth Warburton, Raffald’s most recent housekeeping client. After that, the book contains a substantial preface, likewise dedicated to Warburton. The dedication and preface are both clearly from the perspective of Raffald as they describe her personal experiences as a housekeeper for Warburton. Unlike other books of the time, Raffald writes as a woman, dedicated to a woman, and for a target audience of women. This female focus differentiates "The Experienced English Housekeeper," holding significance in the world of female authorship and publishing.
Scholarly sources about "The Experienced English Housekeeper" indicate that the book serves as a tool to understand the lives of women in the domestic sphere in the eighteenth century. Readers learn about foods consumed, available technologies, and societal expectations. After all, many British women referred to "The Experienced English Housekeeper" as a cultural authority. In particular, the cookbook illuminates the emphasis on thriftiness and resourcefulness among women of the time, who frequently faced economic hardships and lack of financial control at home [8]. Similarly, Raffald provides suggestions regarding cleanliness and order in the house, reinforcing traditional gender roles of the time [9].
Cultural Implications
"The Experienced English Housekeeper" by Elizabeth Raffald boasts enormous cultural significance in England in the eighteenth century and beyond. The book circulated extremely widely as a bestseller of its era. Each copy of "The Experienced English Housekeeper" contains over 900 recipes, a massive collection, especially considering that cookbooks were not as common at the time. Many of these recipes were usually passed down within families, so a publication compiling them together served as a groundbreaking way to share cooking knowledge that previously never appeared in print. Furthermore, some famous British recipes, such as mince pies and Yorkshire puddings, first reached a widespread audience through Raffald's book [7]. Therefore, Raffald spearheaded a number of culinary traditions, inspiring generations of chefs throughout England and the world.
Additionally, "The Experienced English Housekeeper" had functions beyond cooking, providing advice on running a household, entertaining guests, and preparing for special occasions. Raffald's book marked a turning point in the genre of cookbooks, which previously solely focused on recipes [10]. Accordingly, Raffald's book functions as a symbol of the evolution of cookbooks, demonstrating how enduring cultural identities form through distribution of such literature.
Despite the female emphasis in "The Experienced English Housekeeper," the book likely circulated extensively in the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries, reaching an audience of readers that spanned gender, socioeconomic status, and geographic location. The book circulated through booksellers, libraries, and private sales. Unlike other books at the Kislak Center, "The Experienced English Housekeeper" was not rare; in fact, compared to most other books of its era, it was extremely accessible. The recent-looking marginalia from readers like Fritz Blank, Esther Aresty, and James Beard suggests that use cases for "The Experienced English Housekeeper" progressed well into the twentieth century and may even be applicable today.
References
- ↑ Raffald, Elizabeth, and R Baldwin. "The Experienced English Housekeeper." London: Printed for the author, and sold by R. Baldwin, No. 47, in Pater-Noster-Row, 1773. https://franklin.library.upenn.edu/catalog/FRANKLIN_9962183703503681
- ↑ Raffald, Elizabeth. "The Experienced English Housekeeper." London: Printed for R. Baldwin, 1786. https://franklin.library.upenn.edu/catalog/FRANKLIN_9921958233503681
- ↑ Raffald, Elizabeth, and Robert Baldwin. "The Experienced English Housekeeper." London: Printed for R. Baldwin, 1794. https://franklin.library.upenn.edu/catalog/FRANKLIN_9976201983503681
- ↑ Raffald, Elizabeth, and R Baldwin. "The Experienced English Housekeeper." London: Printed for R. Baldwin, 1799. https://franklin.library.upenn.edu/catalog/FRANKLIN_9962129733503681
- ↑ Raffald, Elizabeth, William Osborne, and T Griffin. "The Experienced English Housekeeper." London: Printed for W. Osborne and T. Griffin, 1794. https://franklin.library.upenn.edu/catalog/FRANKLIN_9947852523503681
- ↑ Raffald, Elizabeth, William Osborne, and T Griffin. "The Experienced English Housekeeper." London: Printed for W. Osborne and T. Griffin, 1798. https://franklin.library.upenn.edu/catalog/FRANKLIN_9947825983503681
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Arndt, Alice. "Culinary Biographies." First edition. Houston, Tex.: YES Press, 2006. https://franklin.library.upenn.edu/catalog/FRANKLIN_9940962533503681
- ↑ Theophano, Janet. "Eat My Words: Reading Women’s Lives through the Cookbooks They Wrote." Palgrave, 2002.https://franklin.library.upenn.edu/catalog/FRANKLIN_9978848186403681
- ↑ Wall, Wendy. "Recipes for Thought: Knowledge and Taste in the Early Modern English Kitchen." University of Pennsylvania Press, 2016. https://franklin.library.upenn.edu/catalog/FRANKLIN_9978848186403681
- ↑ Sherman, Sandra. "Invention of the Modern Cookbook." Santa Barbara, Calif.: Greenwood Press, 2010. https://franklin.library.upenn.edu/catalog/FRANKLIN_9978881984403681