EPub
TAC's ePub Page
Introduction
Books. Hardcover, paperback, scrolls...and ePub? Digital platforms and media continue to shape the world around us, and how one reads and experiences a book is no different. Society’s definition of what makes something a book continues to evolve and reshape over time. Gone are the days of curling up on the couch on a rainy day with your favorite book, the pages worn from frequent use and the spine cracked open to your favorite pages. Instead, you grab an electronic device, lacking any of the characteristic remarks of a physical book. The experience one has with reading a book changes. Moreover, what we call a book changes. One digital forum that allows for this aforementioned shift in definition is electronic publishing through ePub. This “eBook standard, designed to work consistently across multiple platforms, devices, and languages,” creates an experience with many similarities as well as differences to a physical book. [1]
What is ePub?
EPub by definition is a format standard for digitally based publications in addition to documents and other media using the “.epub” extension.[2] You can use ePub to create a product that is readable for the general public. It takes lines of code using markup languages, such as HTML or XHTML and presents them as understandable text on a screen. Some common devices that support ePub with this reading include Adobe Digital Editions, iBook, Blue fire, and Aldiko. Electronic publishing came into the public view in 1999, through a format called the “Open eBook Publication Structure,” or OEBPS. [3] This format serves as a set of specifications for the “content, structure, and presentation of electronic books.” [4] Essentially, it is the set of standards required for electronic publishing. The body that selected the standards is a group known as the International Digital Publishing Forum (IDPF), whose mission statement is to “foster global adoption of an open, accessible, interoperable digital publishing ecosystem that enables innovation.” [2] Many iterations of electronic publishing followed OEBPS; in 2007, the IDPF released ePub 2.0.[2] Constant updates to ePub occurred over the years, as can be seen to the right resulting in the current version, ePub 3.1, in 2017. It is anticipated that an ePub 3.2 will be released in the near future.[3]
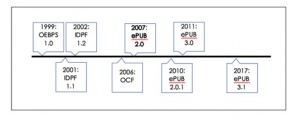
To be called an ePub, a file must contain certain features. These features include using dynamic markup and following a specific order when coding text, though the use of certain semantic markups. [2] ePub specifications also call for protection to rights and the creator, through what is known as Digital Rights Management (DRM). According to William and Mary Law School, DRM is a means to “prevent pirates from stealing and profiting from [others’] work” which in turn “encourages the creation of more content.” [5] These features and specifications, along with others, help characterize ePub differently from other formats.
Materiality
The experiences one has with a physical book in comparison to ePub differs in many facets. One of the first differences noticed between an eBook and a physical book is the physicality of the book. Substrates, paratexts, printing methods, binding—all of these and more contribute to the experience one has when picking up and viewing or reading a book.[6] When looking at a book through a digital platform, the parts that we traditionally think of as making something a book change.
While comparing a digital and a physical book, a key distinction is the materiality of a digital book and how different features of materiality shape readership. To determine the materiality of ePub, it is best to look at the work of Mathew Kirshenbaum. Kirshenbaum is known for coining two frameworks to help define the materiality of the digital. The first framework is forensic materiality: the concept that no two objects are exactly the same, whether that be digital or physical.[7] With digital books, forensic materiality is seen through code. With numerous coding languages and ways to use a platform, each ePub and eBook is unique. Kirshenbaum’s second framework is formal materiality.[7] Formal materiality is the simulation or modeling of materiality via programmed software processes, or more simply put—“instead of manipulating matter, the computer allows us to manipulate symbols.”[7] That is, as symbols are input into a computer through code, we are able to manipulate them in a manner that produces a desirable outcome for the reader and the author.
Just as there are unique characteristics for the creators, the reader can also experience these definitions of materiality. According to behavioral economic theory, people value items more when they have ownership or possession of them.[4] Last modified February 2012.</ref> The sensation of ownership or having something that belongs to oneself creates an inherent value. This can be applied to the materiality shift that occurs with ePub. Each reader is able to create a distinctive reading experience, that though maybe not as the authors originally intended, creates a more materialistic attachment to the book. This increased appreciation for the book arguably achieves the author’s goal for a book to a greater extent, granted that one of the author’s objectives is that the reader truly values the book.
Children’s books serve as a prime example as to evolutions of technology and the experiences that one has when reading a book as a result of differences in materiality. The Wonderful Wizard of Oz is one of the most successful children’s books of all time; the book’s first edition, written in 1900 by L. Frank Baum, is filled with colorful images, illustrated by W.W. Denslow, that draw in and engage readers both young and old.[8] Since the creation of the beloved first edition, numerous versions have been produced, on platforms ranging from audiobook to anniversary print editions to digital books. Here we will compare two editions of the book: a first edition print and an ePub file via Apple iBook.
The reader first notices that the covers and spine of the physical book include vibrant red and green pictures featuring story favorites--the Cowardly Lion, the Tin Man, the Scarecrow, Toto, and of course, Dorothy—providing an introduction to the characters before one even cracks open the spine. These intentional and specific works to the exterior of the book created for a strong contrast to the ePub file, which was downloaded to iBook through the online “Project Gutenberg” database. The ePub cover (see Figure 3) is a plain, red rectangular square with a standard white font stating the title of the book and the name of the author with no other detail. It provides no visual depictions and no contextual evidence as to the premise or characters of the book. Thinking about the intended audience of the book—children—the ePub does not draw in the same excitement and youthful anticipation for what is in store as the first edition does. The lack of a colorful entrance provides no indication for the colorful world that Dorothy enters via tornado. For those readers with no previous knowledge of the book or the subsequent movie, there is no indication as to what is to come in the book; there is also nothing that draws one to this book over another. More than that, it is hard to call the front of the ePub a “cover,” because it does not really differ from any of the other pages of the ePub in any significant way except for the fact that it is at the very front of the eBook.
- Covers of The Wonderful Wizard of Oz
-
Front First Ed.
-
Spine
-
Back
-
ePub cover

There are more material differences to be noted once the reader does open the book. From images of all of the main characters to fields of poppies and illustrations on the copyright and introduction pages of the book, there are no images in the ePub version of the book, leaving the pages of the ePub filled only with words (see Figure 4 and Figure 5). Other major differences between the books include the structure, images, and paratexts. Paratext is “all added written material that does not count as the primary narrative.” [9] In the first edition, this additional written material was crucial. Baum and Denslow laid out each page of the book in a meticulous manner such that images and text are intertwined in a cohesive manner where one can read the words on the page while also seeing a visual depiction of the story as intended by the authors. Denslow’s drawings span across many pages and are drawn in vibrant colors. The nature of these multi-page drawings unifies the words on each individual page even more than what is accomplished simply by reading the text.
With the ePub edition in iBook, by contrast, the reader holds the ability to change the structure and paratext through font, font size, font and page color, and many other elements creating pages that do little to resemble the first edition in any way other than the words on the page (see Figure 7). These differences highlight how ePub and different digital platforms alter the previously thought of conventions of books. Moreover, the changes made to the paratext and other elements of the book remove the intricate uniqueness that helped result in a century of affection for the Wonderful Wizard of Oz. This alters the reading experience as the reader no longer sees the page as the author intended, but rather how the reader chooses to view the page. When reading certain chapters of the book such as Dorothy and her traveling companions in a field of poppy flowers, the page is no longer filled with the colorful red flowers in the ebook as it is in the first edition. Instead, the page is filled with just text, in a font, color, and size of the reader’s choosing. In addition to losing the ability to see the images that the authors envisioned, the reader also loses a sense of what specific words were supposed to be attached to a particular image. By changing the aforementioned size, font, etc., the words on the page shift, changing the number of pages in the eBook. This further alters the reading experience, because moments that Baum and Denslow intended to be on a specific page to create a specific impact or moment can be easily lost. Paragraphs intended to be on a certain page might shift to a different page resulting in a different reading experience than intended by the authors. However, there are benefits to the consumer’s ability to alter the way in which an ePub is read, and that is more accessibility to the general public who may otherwise not have the affordability to read a book as was originally presented by the authors. For example, individuals with the visual impairments can enlarge the font size, color, and shape to make a book more readable and accessible. Thus, though not reading the book in the original material layout that was presented by the authors, the content is still read, and the reader is able to gain some form of appreciation for the works as opposed to not being able to read the book at all. Moreover, as technology continues to advance and develop every day, more and more individuals have access to books like never before. Thus, following Kirshenbaum’s frameworks, both the ePub and the physical book are material objects; additionally, introducing a book to the digital stage can change a large part of what made a book distinctive in its physical form. Important to keep in mind and ask oneself, though, is whether or not these changes are “bad,” or merely different.



Rights and Access
Aforementioned, DRM is a major distinguishing feature of ePub whose purpose is to protect the rights of a content creator so that work that unique work is appreciated as such. In essence, this prevents an individual from simply going online and copying the work of others or using the work of others in a manner not approved by the creator. Two central arguments can be drawn from Digital Rights Management, one with focus on the creator of content, and one with emphasis on consumers of eBooks. The first argument is that as society at large has increasing knowledge and access to the world wide web and all of the spaces available on it, those with some form of a computer coding or data-science background hold the capability to recreate an eBook or text. Whereas, in contrast, with a physical book you must either go rent or buy the book from a store or website to receive a physical copy with an “all-rights reserved” designation, on a digital platform, one could conceivably download or use a text in a manner outside of the author’s intended permission. The second, and contradicting, argument is that by limiting access to the general public, there is an attempt to limit “user choice and innovation.” [10] Furthermore, antagonists of DRM argue that no substantial evidence shows DRM preventing “copyright infringement” and “[keeping] consumers safe from viruses.” Today, there exist organizations such as Electronic Frontier Foundation (EFF), which aims to protect the rights of human privacy while “[preserving] fundamental rights,” and Project Gutenberg, whose mission is to “encourage the creation and distribution of eBooks” by serving as the “first provider of electronic books.” Expanding on this concept presented by Project Gutenberg and EFF, specific questions arise regarding the social aspects associated with an ePub versus a physical book. Personally, book sharing through the library and with friends remains a central part of my childhood memories. I loved visiting the librarians who knew me by name and discovering an exciting new book to learn from. With the restrictions that exist with ePub, one can no longer hand over a great read to a friend or talk to the librarian as he or she stamps the return date into a book. With DRM, this ease in accessibility and social interaction is in a sense removed, altering the dynamic one has with a book. As the notion of access as it relates to books has and continues to change as books move more and more towards the digital, one is left wondering about how far rights and access extend from concepts such as DRM. Next, we will see an example of this extension.
Conclusion
Notes
- ↑ Galey, A. “Enkindling Reciter,”Project Muse 15 (2012): 210-247
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 IDPF. “ePUB Specifications and Projects.” Last modified April 2018. http://www.idpf.org/epub/dir/
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 “A Bit of History.” EDRL Lab, accessed September 28, 2018. https://www.edrlab.org/epub/a-bit-of-history/
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "OEBPS (Open Ebook Forum Publication Structure) 1.2." Library of Congress (2012). Last modified February 2012.
- ↑ Fred Dingledy, “What is Digital Rights Management?” Library Staff Publications (2016): 122 http://scholarship.law.wm.edu/libpubs/122
- ↑ Michelle Levy and Tom Mole. “The Broadview Introduction to Book History,” Broadview Press (2017):6-7.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Matthew G. Kirshenbaum. Mechanisms: New Media and the Forensic Imagination (MIT Press. 2008): 10.
- ↑ Margaret Mackey, “The Survival of Engaged Reading in the Internet Age: New Media, Old Media, and the Book,” Children’s Literature in Education vol. 32(2001): 167. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010498001725
- ↑ “Paratext.” Georgetown University, accessed October 14, 2018. http://narrative.georgetown.edu/wiki/index.php/Paratext
- ↑ DRM.” Electronic Frontier Foundation, accessed October 13, 2018.[1]






